Quickstart in Couchbase with Java and Spring Data
- Learn to build a REST API in Java using Spring Data and Couchbase
- Explore key-based operations and SQL++ querying using Spring Data Couchbase repositories
- Explore CRUD operations in action with Couchbase
Getting Started
Prerequisites
To run this prebuilt project, you will need:
- Couchbase Capella cluster with travel-sample bucket loaded.
- To run this tutorial using a self managed Couchbase cluster, please refer to the appendix.
- Git
- Code Editor or an Integrated Development Environment (e.g., Eclipse)
- Java SDK 17 or higher installed
- Gradle Build Tool
Source Code
The sample source code used in this tutorial is published on GitHub. To obtain it, clone the git repository with your IDE or execute the following command:
git clone https://github.com/couchbase-examples/java-springdata-quickstart.gitInstall Dependencies
Gradle dependencies:
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
// spring data couchbase connector
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase'
// swagger ui
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-ui:1.6.6'Useful Links
Database Server Configuration
Spring Data Couchbase connector can be configured by providing a @Configuration bean that extends AbstractCouchbaseConfiguration.
The sample application provides a modernized configuration bean with improved error handling and environment variable support:
@Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableCouchbaseRepositories
public class CouchbaseConfiguration extends AbstractCouchbaseConfiguration {
@Value("#{systemEnvironment['DB_CONN_STR'] ?: '${spring.couchbase.bootstrap-hosts:localhost}'}")
private String host;
@Value("#{systemEnvironment['DB_USERNAME'] ?: '${spring.couchbase.bucket.user:Administrator}'}")
private String username;
@Value("#{systemEnvironment['DB_PASSWORD'] ?: '${spring.couchbase.bucket.password:password}'}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.couchbase.bucket.name:travel-sample}")
private String bucketName;
@Override
public String getConnectionString() {
return host;
}
@Override
public String getUserName() {
return username;
}
@Override
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public String getBucketName() {
return bucketName;
}
@Override
public String typeKey() {
return "type";
}
@Override
@Bean(destroyMethod = "disconnect")
public Cluster couchbaseCluster(ClusterEnvironment couchbaseClusterEnvironment) {
try {
log.debug("Connecting to Couchbase cluster at " + host);
return Cluster.connect(getConnectionString(), getUserName(), getPassword());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error connecting to Couchbase cluster", e);
throw e;
}
}
@Bean
public Bucket getCouchbaseBucket(Cluster cluster) {
try {
if (!cluster.buckets().getAllBuckets().containsKey(getBucketName())) {
log.error("Bucket with name {} does not exist. Creating it now", getBucketName());
throw new BucketNotFoundException(bucketName);
}
return cluster.bucket(getBucketName());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error getting bucket", e);
throw e;
}
}
}from config/CouchbaseConfiguration.java
These methods are used to configure and retrieve a Couchbase Cluster and a specific Bucket within that cluster in a Spring application.
-
couchbaseCluster(ClusterEnvironment couchbaseClusterEnvironment): This method configures and returns a Cluster instance using the provided ClusterEnvironment. It logs a debug message indicating the connection attempt to the Couchbase cluster. If an error occurs during the connection attempt, it logs an error message and rethrows the exception. -
getCouchbaseBucket(Cluster cluster): This method retrieves a specific Bucket from the given Cluster. It first checks if the bucket exists in the cluster by calling cluster.buckets().getAllBuckets().containsKey(getBucketName()). If the bucket does not exist, it logs an error message, throws a BucketNotFoundException, and stops the application startup. Otherwise, it returns the Bucket instance.
This default configuration assumes that you have a locally running Couchbae server and uses standard administrative login and password for demonstration purpose. Applications deployed to production or staging environments should use less privileged credentials created using Role-Based Access Control. Please refer to Managing Connections using the Java SDK with Couchbase Server for more information on Capella and local cluster connections.
Application Properties
You need to configure the connection details to your Couchbase Server in the application.properties file located in the src/main/resources directory.s
Modern Spring Boot 3.5+ Configuration:
# Modern Couchbase configuration
spring.couchbase.connection-string=${DB_CONN_STR}
spring.couchbase.username=${DB_USERNAME}
spring.couchbase.password=${DB_PASSWORD}
spring.couchbase.bucket.name=travel-sample
# Connection optimizations
spring.couchbase.env.timeouts.query=30000ms
spring.couchbase.env.timeouts.key-value=5000ms
spring.couchbase.env.timeouts.connect=10000msEnvironment Variables Setup
For security, use a .env file in your project root:
DB_CONN_STR=couchbases://xyz.cloud.couchbase.com
DB_USERNAME=your_username
DB_PASSWORD=your_passwordThe connection string formats:
- Couchbase Capella:
couchbases://xyz.cloud.couchbase.com(secure) - Local Couchbase:
couchbase://localhost(non-secure)
The couchbases:// protocol is used for secure TLS connections (required for Couchbase Capella). The couchbase:// protocol is for non-secure local connections.
Running the Application
Directly on Machine
At this point, we have installed the dependencies, loaded the travel-sample data and configured the application with the credentials. The application is now ready and you can run it.
./gradlew bootRunNote: If you're using Windows, you can run the application using the Gradle wrapper batch file:
.\gradlew.bat bootRunUsing Docker
Build the Docker image
docker build -t java-springdata-quickstart .Run the Docker image
docker run -d --name springdata-container -p 8080:8080 java-springdata-quickstartNote: The application.properties file has the connection information to connect to your Capella cluster. You can also pass the connection information as environment variables to the Docker container.
If you choose not to pass the environment variables, you can update the application.properties file in the src/main/resources folder.
Once the application is running, you can see the logs in the console. You should see the following log message indicating that the application has started successfully:
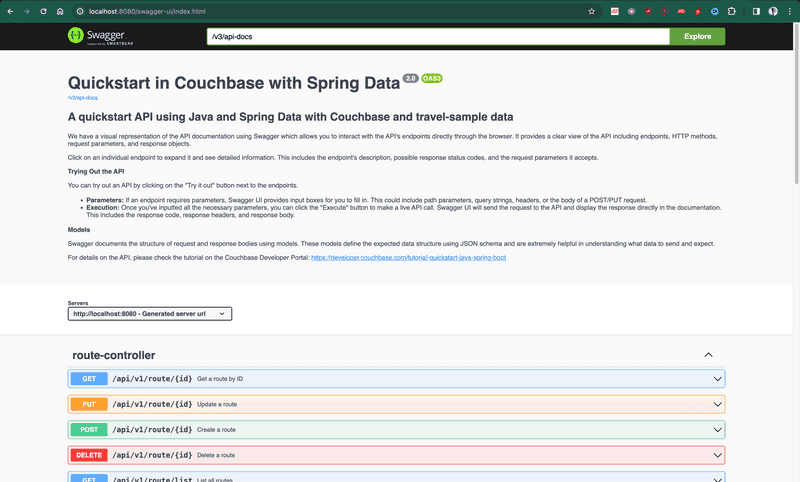
Once the site is up and running, you can launch your browser and go to the Swagger Start Page to test the APIs.
Data Model
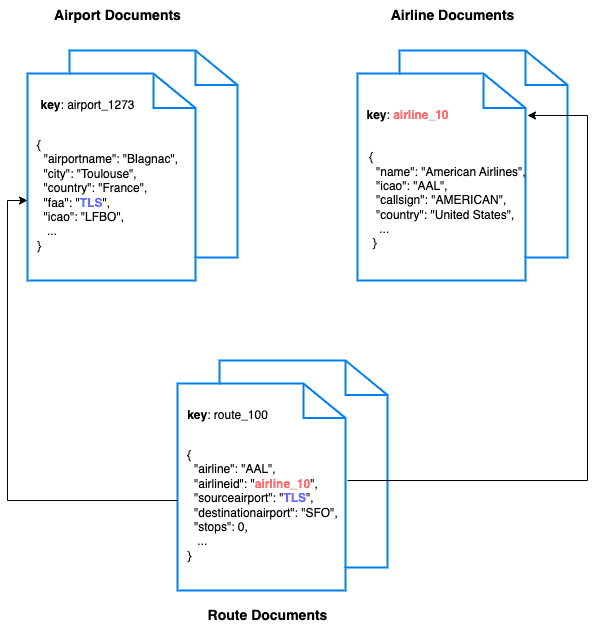
For this tutorial, we use three collections, airport, airline and route that contain sample airports, airlines and airline routes respectively. The route collection connects the airports and airlines as seen in the figure below. We use these connections in the quickstart to generate airports that are directly connected and airlines connecting to a destination airport. Note that these are just examples to highlight how you can use SQL++ queries to join the collections.
Airline Document Structure
We will be setting up a REST API to manage some airline documents. Our airline document will have a structure similar to the following:
{
"name": "Couchbase Airways",
"callsign": "Couchbase",
"iata": "CB",
"icao": "CBA",
"country": "United States"
}The name field is the name of the airline. The callsign field is the callsign of the airline. The iata field is the IATA code of the airline. The icao field is the ICAO code of the airline. The country field is the country of the airline.
Let's Review the Code
To begin clone the repo and open it up in the IDE of your choice to learn about how to create, read, update and delete documents in your Couchbase Server.
Code Organization
src/test/java: Contains integration tests.src/main/java/org/couchbase/quickstart/springdata/repository: Contains the repository implementation.src/main/java/org/couchbase/quickstart/springdata/model: Contains the data model.src/main/java/org/couchbase/quickstart/springdata/controller: Contains the RESTful API controllers.src/main/java/org/couchbase/quickstart/springdata/service: Contains the service classes.
Repository
AirlineRepository.java
This interface extends the CouchbaseRepository interface and provides methods for CRUD operations.
-
@Scope("..."):Specifies the scope of the repository, which helps organize and manage documents within a Couchbase bucket. -
@Collection("..."):Specifies the collection within the bucket where the documents are stored. -
@Repository:Marks the interface as a repository component in the Spring application context. -
@ScanConsistency(query = QueryScanConsistency.REQUEST_PLUS): Specifies the scan consistency level for queries executed by methods in this repository, ensuring strong consistency for read operations.
Model
Airline.java
This class represents an airline document. The @Document annotation indicates that this class is a Couchbase document. The @Field annotation indicates that the following fields are Couchbase document fields: name, callsign, iata, icao, country.
Controller
AirlineController.java
This class contains the REST API endpoints for CRUD operations. The @RestController annotation indicates that this class is a REST controller. The @RequestMapping annotation specifies the base URL for the REST API. The @Autowired annotation is used to autowire the AirlineService object. The @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, and @DeleteMapping annotations are used to map HTTP GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE requests respectively to their corresponding methods.
Service
AirlineService.java
This class contains the business logic for the REST API. The @Autowired annotation is used to autowire the AirlineRepository object.
Mapping Workflow
Mapping workflows describe how the HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) interact with the AirlineService and the underlying database through the AirlineRepository to perform various operations on airline data.
A simple REST API using Spring Boot and the Couchbase SDK version 3.x with the following endpoints:
- Retrieve airlines by ID.
- Create new airlines with essential information.
- Update airline details.
- Delete airlines.
- List all airlines with pagination.
- List airlines by country.
- List airlines by destination airport.
GET Mapping Workflow
- The client initiates a GET request to
/api/v1/airline/{id}, providing the unique identifier ({id}) of the airline they want to retrieve. - The
AirlineControllerreceives the request and invokes thegetAirlineById(id)method in theAirlineService. This function internally calls the findById method of theAirlineRepository(which extendsCouchbaseRepository) to retrieve the airline information from the Couchbase database. - Inside the
AirlineService, the request is processed. The service interacts with theAirlineRepository. - The
AirlineRepositoryexecutes a query against the Couchbase database to retrieve the airline information based on the provided ID. - If the airline is found, the
AirlineServicereturns the retrieved information to theAirlineController. - The
AirlineControllersends an HTTP response with an HTTP status code of200(OK) and includes the airline information in the response body. - If the airline is not found in the database, the
AirlineServicereturnsnull. - The
AirlineControllerresponds with an HTTP status code of404(Not Found) if the airline is not found.
POST Mapping Workflow
- The client initiates a POST request to
/api/v1/airline/{id}with a JSON payload containing the airline's information, including a unique ID. - The
AirlineControllerreceives the request and invokes thecreateAirline(airline)method in theAirlineService. ThecreateAirlinemethod internally calls the save method of theAirlineRepositoryto save the airline information to the Couchbase database. - Inside the
AirlineService, the incoming data is validated to ensure it meets the required criteria. - The
AirlineServicecreates a newAirlineobject and saves it to the Couchbase database using theAirlineRepository. - If the airline is successfully created, the
AirlineServicereturns the newly created airline object. - The
AirlineControllersends an HTTP response with an HTTP status code of201(Created), including the newly created airline information in the response body. - If the airline already exists in the database, a
DocumentExistsExceptionmay be thrown. - In case of a conflict, the
AirlineControllerresponds with an HTTP status code of409(Conflict).
PUT Mapping Workflow
- The client initiates a PUT request to
/api/v1/airline/{id}with a JSON payload containing the updated airline information and the unique ID of the airline to be updated. - The
AirlineControllerreceives the request and invokes theupdateAirline(id, airline)method in theAirlineService. TheupdateAirlinemethod internally calls the save method of theAirlineRepositoryto update the airline information in the Couchbase database. - Inside the
AirlineService, the incoming data is validated to ensure it meets the required criteria. - The
AirlineServiceupdates the airline record in the Couchbase database using theAirlineRepository. - If the airline is found and updated successfully, the
AirlineServicereturns the updated airline object. - The
AirlineControllersends an HTTP response with an HTTP status code of200(OK), including the updated airline information in the response body. - If the airline is not found in the database, the
AirlineServicereturnsnull. - In case of an update to a non-existent airline, the
AirlineControllerresponds with an HTTP status code of404(Not Found).
DELETE Mapping Workflow
- The client initiates a DELETE request to
/api/v1/airline/{id}, specifying the unique identifier ({id}) of the airline to be deleted. - The
AirlineControllerreceives the request and invokes thedeleteAirline(id)method in theAirlineService. ThedeleteAirlinemethod internally calls the deleteById method of theAirlineRepositoryto delete the airline from the Couchbase database. - Inside the
AirlineService, the service attempts to find and delete the airline record from the Couchbase database using theAirlineRepository. - If the airline is found and successfully deleted, the
AirlineServicecompletes the operation. - The
AirlineControllerresponds with an HTTP status code of204(No Content) to indicate a successful deletion. - If the airline is not found in the database, the
AirlineServicemay throw aDocumentNotFoundException. - In case the airline is not found, the
AirlineControllerresponds with an HTTP status code of404(Not Found).
These detailed workflows provide a comprehensive understanding of how each mapping is handled by the controller, service, and repository components in your Spring Data project.
Custom SQL++ Queries
The AirlineRepository interface contains a @Query annotation that allows us to create custom N1QL queries. The @ScanConsistency annotation allows us to specify the scan consistency for the query. The @Param annotation allows us to specify parameters for the query.
@Query("#{#n1ql.selectEntity} WHERE #{#n1ql.filter} AND country = $country")
@ScanConsistency(query = QueryScanConsistency.REQUEST_PLUS)
List<Airline> findByCountry(@Param("country") String country);from repository/AirlineRepository.java
The findByCountry method returns a list of airlines by country. It uses the @Query annotation to create a custom N1QL query. The @Param annotation is used to specify the country parameter for the query. The @ScanConsistency annotation is used to specify the scan consistency for the query.
@Query("#{#n1ql.selectEntity} WHERE #{#n1ql.filter} AND ANY destination IN routes SATISFIES destination = $airport END")
@ScanConsistency(query = QueryScanConsistency.REQUEST_PLUS)
List<Airline> findByDestinationAirport(@Param("airport") String airport);from repository/AirlineRepository.java
The findByDestinationAirport method returns a list of airlines by destination airport. It uses the @Query annotation to create a custom N1QL query. The @Param annotation is used to specify the airport parameter for the query. The @ScanConsistency annotation is used to specify the scan consistency for the query.
For more information, see the Couchbase Java SDK documentation.
Running The Tests
Integration Tests
This project uses Gradle with comprehensive integration test setup. The tests connect to a real Couchbase instance:
./gradlew testWindows users:
.\gradlew.bat testTest Reliability
This project was modernized to ensure reliable test execution:
- Tests properly connect to Couchbase and validate real data
- Integration tests are included in the standard test run
- Test logging provides clear visibility into execution
Continuous Integration
GitHub Actions
The project includes a modern GitHub Actions workflow with:
- Multi-Version Testing: Java 17 and 21 support
- Manual Triggering:
workflow_dispatchfor on-demand runs - Enhanced Reliability: 15-minute timeouts, non-blocking failure handling
- Test Artifacts: Automatic test report uploads
- Optimized Commands: Uses
./gradlew clean test --stacktrace
CI/CD Features
The workflow provides:
- Temurin JDK setup with Gradle caching
- Real integration test execution against Couchbase
- Test result artifact collection for debugging
- Slack notification integration (configurable)
Project Setup Notes
This project was created using the Spring Initializr and modernized with:
- Project: Gradle Project with Wrapper
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: 3.5.5 (upgraded from 2.7.18)
- Packaging: Jar
- Java Version: 17+ (upgraded from Java 8)
- Key Dependencies:
- Spring Boot Starter Web
- Spring Boot Starter Data Couchbase
- SpringDoc OpenAPI Starter WebMVC UI
- Spring Boot Starter Validation
- Project Lombok
- JUnit 5 (Jupiter)
Performance Optimizations: The project uses Slice instead of Page for better memory efficiency and eliminates expensive COUNT queries in pagination scenarios.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome! If you'd like to contribute to this project, please fork the repository and create a pull request.
Appendix
Extending API by Adding New Entity
If you would like to add another entity to the APIs, these are the steps to follow:
- Create the new entity (collection) in the Couchbase bucket. You can create the collection using the SDK or via the Couchbase Server interface.
- Define the mappings in a new file in the
controllersfolder similar to the existing mappings likeAirportController.java. - Define the service in a new file in the
servicesfolder similar to the existing services likeAirportService.java. - Define the repository in a new file in the
repositoriesfolder similar to the existing repositories likeAirportRepository.java. - For integration tests, create a new class in the
controllerspackage similar to the existing tests likeAirportIntegrationTest.java.
Running Self Managed Couchbase Cluster
If you are running this quickstart with a self managed Couchbase cluster, you need to load the travel-sample data bucket in your cluster and generate the credentials for the bucket.
You need to update the connection string and the credentials in the src/main/resources/application.properties file.
NOTE: Couchbase must be installed and running prior to running the Spring Boot app.
Swagger Documentation
Swagger documentation provides a clear view of the API including endpoints, HTTP methods, request parameters, and response objects.
Click on an individual endpoint to expand it and see detailed information. This includes the endpoint's description, possible response status codes, and the request parameters it accepts.
Trying Out the API
You can try out an API by clicking on the "Try it out" button next to the endpoints.
-
Parameters: If an endpoint requires parameters, Swagger UI provides input boxes for you to fill in. This could include path parameters, query strings, headers, or the body of a POST/PUT request.
-
Execution: Once you've inputted all the necessary parameters, you can click the "Execute" button to make a live API call. Swagger UI will send the request to the API and display the response directly in the documentation. This includes the response code, response headers, and response body.
Models
Swagger documents the structure of request and response bodies using models. These models define the expected data structure using JSON schema and are extremely helpful in understanding what data to send and expect.