Build PDF Chat App With Nvidia NIM, LLama3 and Couchbase Python SDK
- Construct a PDF Chat App with LangChain, Nvidia NIM, Meta LLama3, Couchbase Vector Search, and Streamlit.
- Learn to upload PDFs into Couchbase Vector Store with LangChain and Nvidia Embeddings.
- Discover how to use RAG for context-based Q&A from PDFs using Nvidia NIM and Meta LLama3.
Introduction
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on constructing an AI-enhanced Chat Application. We will create a dynamic chat interface capable of delving into PDF documents to extract and provide summaries, key facts, and answers to your queries. By the end of this tutorial, you'll have a powerful tool at your disposal, transforming the way you interact with and utilize the information contained within PDFs.
This tutorial will demonstrate how to -
- Construct a Couchbase Search Index for doing Vector Search.
- Chunk PDFs into Vectors with LangChain and use Couchbase Vector Store to store the vectors into Couchbase.
- Query large language models via the RAG framework for contextual insights. We will use NVidia NIM for generating Embeddings and LLM with model from Meta's LLama series.
- Craft an elegant UI with Streamlit. All these components come together to create a seamless, AI-powered chat experience.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.10 or higher installed.
- Ensure that the Python version is compatible with the Couchbase SDK.
- Couchbase Cluster (Self Managed or Capella) version 7.6+ with Search Service
- API Key for Nvidia NIM. You can get it from Nvidia NIM build website. It is more discussed in the Method to get Nvidia NIM API Key.
Note that this tutorial is designed to work with the latest Python SDK version (4.2.0+) for Couchbase. It will not work with the older Python SDK versions.
Vector Search in Couchbase is only supported at Couchbase Version 7.6+.
Method to get Nvidia NIM API Key
- Head over to https://build.nvidia.com/ which is the Nvidia NIM cloud website.
- Search any model, like you may go to LLama 3 Model.
- At the experience tab, there will be a chat window and a code window which is running. On the top right of code window, you will find an option to Get API Key
- Fill in your details, register and get access to Nvidia's API Key to build stuff using their NIM architecture.
Quick Start Guide:
Cloning Repo
git clone https://github.com/couchbase-examples/nvidia-rag-demo.gitInstall Dependencies
Any dependencies should be installed through pip, the default package manager for Python. You may use virtual environment as well.
python -m pip install -r requirements.txtSetup Database Configuration
Capella Setup
To know more about connecting to your Capella cluster, please follow the instructions.
Specifically, you need to do the following:
- Create the database credentials to access cluster via SDK
- Allow access to the Cluster from the IP on which the application is running.
Self Managed Setup
- Follow Couchbase Installation Options for installing the latest Couchbase Database Server Instance. Make sure to add the Search Service.
Create Bucket
- For the purpose of this tutorial, we will be using specific bucket, scope and collection. However, you may use any name of your choice but make sure to update names in all the steps.
- Create a bucket named
pdf-chat. We will use the_defaultscope and_defaultcollection of this bucket.
Create the Search Index on Full Text Service
We need to create the Search Index on the Full Text Service in Couchbase. For this demo, you can import the following index using the instructions.
-
- Copy the index definition to a new file index.json.
- Import the file in Capella using the instructions in the documentation.
- Click on Create Index to create the index.
-
- Click on Search -> Add Index -> Import.
- Copy the following Index definition in the Import screen.
- Click on Create Index to create the index.
You may also create a vector index using Search UI on both Couchbase Capella and Couchbase Self Managed Server.
Index Definition
Here, we are creating the index pdf_search on the documents. The Vector field is set to embedding with 1024 dimensions based on NV-Embed Model's output Dimnesions and the text field set to text. We are also indexing and storing all the fields under metadata in the document as a dynamic mapping to account for varying document structures. The similarity metric is set to dot_product. If there is a change in these parameters, please adapt the index accordingly.
{
"name": "pdf_search",
"type": "fulltext-index",
"params": {
"doc_config": {
"docid_prefix_delim": "",
"docid_regexp": "",
"mode": "scope.collection.type_field",
"type_field": "type"
},
"mapping": {
"default_analyzer": "standard",
"default_datetime_parser": "dateTimeOptional",
"default_field": "_all",
"default_mapping": {
"dynamic": true,
"enabled": false
},
"default_type": "_default",
"docvalues_dynamic": false,
"index_dynamic": true,
"store_dynamic": false,
"type_field": "_type",
"types": {
"_default._default": {
"dynamic": true,
"enabled": true,
"properties": {
"embedding": {
"enabled": true,
"dynamic": false,
"fields": [
{
"dims": 1024,
"index": true,
"name": "embedding",
"similarity": "dot_product",
"type": "vector",
"vector_index_optimized_for": "recall"
}
]
},
"metadata": {
"dynamic": true,
"enabled": true
},
"text": {
"enabled": true,
"dynamic": false,
"fields": [
{
"index": true,
"name": "text",
"store": true,
"type": "text"
}
]
}
}
}
}
},
"store": {
"indexType": "scorch",
"segmentVersion": 16
}
},
"sourceType": "gocbcore",
"sourceName": "pdf-chat",
"sourceParams": {},
"planParams": {
"maxPartitionsPerPIndex": 64,
"indexPartitions": 16,
"numReplicas": 0
}
}Setup Environment Config
Copy the secrets.example.toml file in .streamlit folder and rename it to secrets.toml and replace the placeholders with the actual values for your environment. All configuration for communication with the database is read from the environment variables.
NVIDIA_API_KEY = "<nvidia_nim_api_key>"
DB_CONN_STR = "<connection_string_for_couchbase_cluster>"
DB_USERNAME = "<username_for_couchbase_cluster>"
DB_PASSWORD = "<password_for_couchbase_cluster>"
DB_BUCKET = "<name_of_bucket_to_store_documents>"
DB_SCOPE = "<name_of_scope_to_store_documents>"
DB_COLLECTION = "<name_of_collection_to_store_documents>"
INDEX_NAME = "<name_of_fts_index_with_vector_support>"
LOGIN_PASSWORD = "<password to access the streamlit app>"Nvidia NIM API Key is required for usage in generating embedding and querying LLM.
The connection string expects the
couchbases://orcouchbase://part.
For this tutorial,
DB_BUCKET = pdf-chat,DB_SCOPE = _default,DB_COLLECTION = _defaultandINDEX_NAME = pdf_search.
Login_Password of Streamlit app is a basic password to access the app. You can set the password here and while using the app, password will be required to access the app.
Running the Application
After starting Couchbase server, adding vector index and installing dependencies. Our Application is ready to run.
In the projects root directory, run the following command
streamlit run chat_with_pdf.pyThe application will run on your local machine at http://localhost:8501.
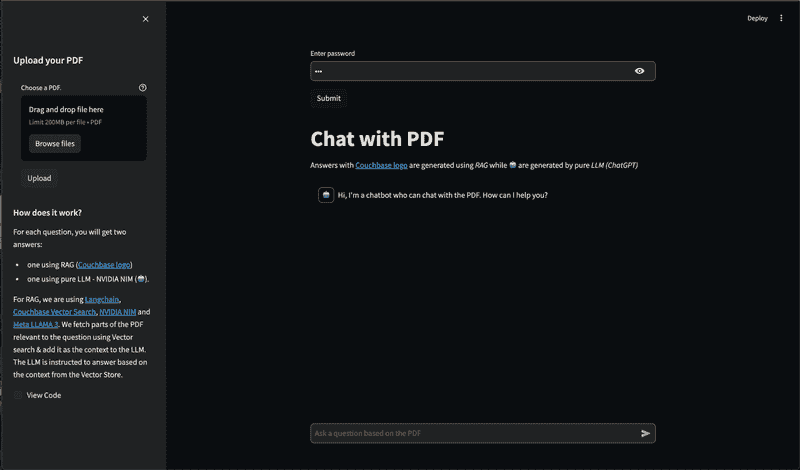
Using PDF Chat App
The page starts with a text box to enter your login password. This is the same password defined earlier in the Setup Environment Config section. After submitting the password, the main application page will open.
On the left sidebar, you'll find an option to upload a PDF document you want to use with this PDF Chat App. Depending on the size of the PDF, the upload process may take some time.
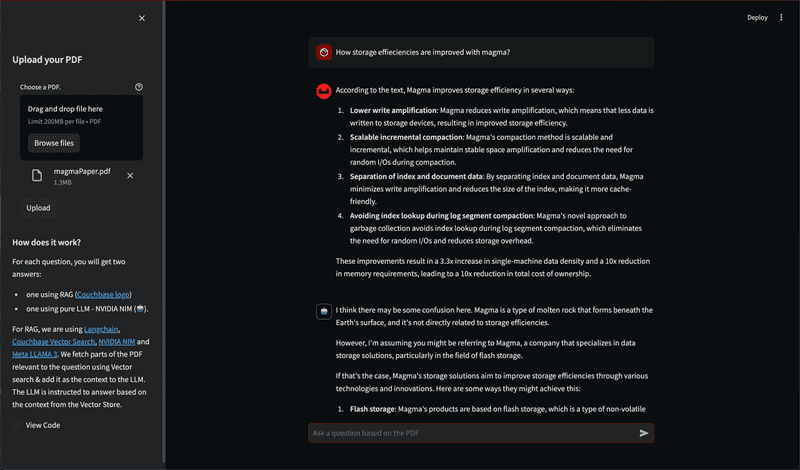
In the main area, there's a chat screen where you can ask questions about the uploaded PDF document. You will receive two responses: one with context from the PDF (Couchbase Logo - ) , and one without the PDF context (Bot Logo - 🤖). This demonstrates how the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) model enhances the answers provided by the language model using the PDF content.
In the below image, notice how the result with bot image is hallucinating with different results like Molten Lava and Magma Data Company where as with RAG result, we are getting much more to the point result.
Concepts
The PDF Chat application leverages two powerful concepts: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Vector Search. Together, these techniques enable efficient and context-aware interactions with PDF documents.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is like having two helpers:
- Retriever: This helper looks through all the PDF documents to find the most relevant information based on your question or prompt.
- Generator: This helper is like a large language model (e.g., GPT-4, Gemini, LLama3) that can understand natural language and generate human-like responses.
Here's how RAG works:
- You ask a question or provide a prompt to the app.
- The Retriever helper goes through the PDF documents and finds the most relevant passages or sections related to your question using Vector Search.
- The Generator helper takes those relevant passages and your original question, and uses them to generate a clear and contextual answer.
This enhances the context from PDF and LLM is able to give relevant results from the PDF rather than giving generalized results.
Vector Search with Couchbase
Couchbase is a NoSQL database that provides a powerful Vector Search capability. It allows you to store and search through high-dimensional vector representations (embeddings) of textual data, such as PDF content.
The PDF Chat app uses LangChain to convert the text from the PDF documents into embeddings. These embeddings are then stored in a Couchbase bucket, along with the corresponding text.
When a user asks a question or provides a prompt:
- The app converts the user's query into an embedding using LangChain's embedding models (e.g., Nvidia's NV-Embed-QA embeddings).
- Couchbase's Vector Search capability is utilized, which supports search indexes. A dedicated search index is created for the PDF embeddings and their corresponding text content, configured with the necessary indexing parameters (bucket, scope, collection, index name).
- The app queries this search index using the user's query embedding. Couchbase's Vector Search calculates the similarity (e.g., dot product) between the query embedding and the indexed PDF embeddings, enabling fast retrieval of the nearest neighbor embeddings.
- The nearest neighbor embeddings represent the most semantically similar passages or sections from the PDF documents compared to the user's query.
- The app retrieves the text content associated with these nearest neighbor embeddings, providing the necessary context for generating a relevant response.
- Couchbase's Vector Search supports advanced indexing techniques, such as scoped indexes, dynamic indexing and hybrid search, allowing for efficient management, better scaling of the vector store and multiple types of search supported.
- The search index facilitates fast and accurate retrieval, enabling the app to provide context-aware and relevant responses to the user's queries, even when the phrasing or terminology differs from the PDF content.
- Couchbase's Vector Search integrates seamlessly with LangChain's CouchbaseSearchVectorStore class, abstracting away the complexities of vector similarity calculations.
LangChain
LangChain is a powerful library that simplifies the process of building applications with large language models (LLMs) and vector stores like Couchbase.
In the PDF Chat app, LangChain is used for several tasks:
- Loading and processing PDF documents: LangChain's PDFLoader is used to load the PDF files and convert them into text documents.
- Text splitting: LangChain's RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter is used to split the text from the PDF documents into smaller chunks or passages, which are more suitable for embedding and retrieval.
- Embedding generation: LangChain integrates with various embedding models, such as Nvidia QA Embedding Models embeddings, to convert the text chunks into embeddings.
- Vector store integration: LangChain provides a CouchbaseSearchVectorStore class that seamlessly integrates with Couchbase's Vector Search, allowing the app to store and search through the embeddings and their corresponding text.
- Chains: LangChain provides various chains for different requirements. For using RAG concept, we require Retrieval Chain for Retrieval and Question Answering Chain for Generation part. We also add Prompts that guide the language model's behavior and output. These all are combined to form a single chain which gives output from user questions.
- Streaming Output: LangChain supports streaming, allowing the app to stream the generated answer to the client in real-time.
Nvidia NIM
NVIDIA NIM is a set of easy-to-use inference microservices for accelerating the deployment of foundation models on any cloud or data center and helping to keep your data secure. This set of accelerated inference microservices allows organizations to run AI models anywhere - in the cloud, data center, workstations, and PCs. You may learn more about using Nvidia NIM with Langchain here
Here are some of its benefits:
- Simplifying Development: NIM simplifies the development of AI applications by providing developers with industry-standard APIs. These APIs are compatible with popular large language model (LLM) development frameworks, making it easy to integrate AI models into your application.
- Seamless Integration: NIM containers seamlessly integrate with the Kubernetes (K8s) ecosystem and many others. This integration allows efficient orchestration and management of containerized AI applications, facilitating seamless AI inferencing at scale.
- Optimized Performance: NVIDIA NIM leverages optimized inference engines from NVIDIA and the community, including TensorRT, TensorRT-LLM, Triton Inference Server, and more. These engines improve AI application performance and efficiency while delivering lower-latency, high-throughput inference
- Customizable and Secure: Developers can easily customize NIM by deploying models fine-tuned to deliver the best accuracy for their specific use case. Moreover, NIM ensures the security and control of generative AI applications and data with prebuilt, cloud-native microservices.
By combining Vector Search with Couchbase, RAG, and LangChain; the PDF Chat app can efficiently ingest PDF documents, convert their content into searchable embeddings, retrieve relevant information based on user queries and conversation context, and generate context-aware and informative responses using large language models. These LLMs run on Nvidia NIM infrastructure to provide simple and fast inferences. This approach provides users with a powerful and intuitive way to explore and interact with large PDF files.
Let us Understand the Flow
To begin this tutorial, clone the repo and open it up in the IDE of your choice. Now you can learn how to create the PDF Chat App. The whole code is written in chat_with_pdf.py file.
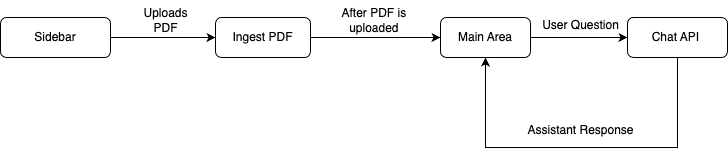
App Flow
The fundamental workflow of the application is as follows: The user initiates the process from the Main Page's sidebar by uploading a PDF. This action triggers the save_to_vector_store function, which subsequently uploads the PDF into the Couchbase vector store. Following this, the user can now chat with the LLM.
On the Chat Area, the user can pose questions. These inquiries are processed by the Chat API, which consults the LLM for responses, aided by the context provided by RAG. The assistant then delivers the answer, and the user has the option to ask additional questions.
Connecting to Couchbase
The first step will be connecting to Couchbase. Couchbase Vector Search is required for PDF Upload as well as during chat (For Retrieval). We will use the Couchbase Python SDK to connect to the Couchbase cluster. The connection is established in the connect_to_couchbase function.
The connection string and credentials are read from the environment variables. We perform some basic required checks for the environment variable not being set in the secrets.toml, and then proceed to connect to the Couchbase cluster. We connect to the cluster using connect method.
def connect_to_couchbase(connection_string, db_username, db_password):
"""Connect to Couchbase"""
from couchbase.cluster import Cluster
from couchbase.auth import PasswordAuthenticator
from couchbase.options import ClusterOptions
from datetime import timedelta
auth = PasswordAuthenticator(db_username, db_password)
options = ClusterOptions(auth)
connect_string = connection_string
cluster = Cluster(connect_string, options)
# Wait until the cluster is ready for use.
cluster.wait_until_ready(timedelta(seconds=5))
return clusterInitialize Embeddings and Couchbase Vector Store
We will now initialize Nvidia Embed QA 4 Model powered by langchain integration which will be used by CouchbaseSearchVectorStore for converting the split docs defined above to vectors (embeddings).
We will also initialize Couchbase vector store with Couchbase bucket info. Firstly we will connect to Couchbase cluster using connect_to_couchbase method.
We will define the bucket, scope, collection and index names from Environment Variables.
# Use Nvidia's embeddings model
embedding = NVIDIAEmbeddings(
nvidia_api_key=os.getenv("NVIDIA_API_KEY"),
model="NV-Embed-QA")
# Connect to Couchbase Vector Store
cluster = connect_to_couchbase(DB_CONN_STR, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD)
vector_store = get_vector_store(
cluster,
DB_BUCKET,
DB_SCOPE,
DB_COLLECTION,
embedding,
INDEX_NAME,
)We are using get_vector_store method which initializes LangChain's CouchbaseSearchVectorStore
def get_vector_store(
_cluster,
db_bucket,
db_scope,
db_collection,
_embedding,
index_name,
):
"""Return the Couchbase vector store"""
vector_store = CouchbaseSearchVectorStore(
cluster=_cluster,
bucket_name=db_bucket,
scope_name=db_scope,
collection_name=db_collection,
embedding=_embedding,
index_name=index_name,
)
return vector_storeUploading And Ingesting PDF
save_to_vector_store function takes care of uploading the PDF file in vector format to Couchbase Database using CouchbaseSearchVectorStore in LangChain. It splits text into small chunks, generate embeddings for those chunks, and ingest the chunks and their embeddings into a Couchbase vector store. Let's go step by step on how it does.
Upload PDF
This part of code creates a file uploader on sidebar using Streamlit library. After PDF is uploaded, save_to_vector_store function is called to further process the PDF.
with st.form("upload pdf"):
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader(
"Choose a PDF.",
help="The document will be deleted after one hour of inactivity (TTL).",
type="pdf",
)
submitted = st.form_submit_button("Upload")
if submitted:
# store the PDF in the vector store after chunking
save_to_vector_store(uploaded_file, vector_store)Read and Load Uploaded PDF
This function ensures that the uploaded PDF file is properly handled, loaded, and prepared for storage or processing in the vector store. It first checks if file was actually uploaded. Then the uploaded file is saved to a temporary file in binary format.
From the temporary file, PDF is loaded in PyPDFLoader from the LangChain library which loads the PDF into LangChain Document Format
def save_to_vector_store(uploaded_file, vector_store):
"""Chunk the PDF & store it in Couchbase Vector Store"""
if uploaded_file is not None:
temp_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
temp_file_path = os.path.join(temp_dir.name, uploaded_file.name)
with open(temp_file_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(uploaded_file.getvalue())
loader = PyPDFLoader(temp_file_path)
docs = loader.load()Add Documents to Vector Store
We will utilize the vector store created at Initialize Embeddings and Couchbase Vector Store. In this we will add the documents using add_documents method of Couchbase vector store. This method will utilize the Nvidia's Embed QA Model to create embeddings(vectors) from text and add it to Couchbase documents in the specified collection.
vector_store.add_documents(docs)Chat With PDF
After uploading the PDF into Couchbase, we are now ready to utilize the power of Couchbase Vector Search, RAG and LLM to get context based answers to our questions. When the user asks a question. The assistant (LLM) is called here with RAG context, the response from the assistant is sent back to the user.
LangChain Expression Language (LCEL)
We will now utilize the power of LangChain Chains using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL). LCEL makes it easy to build complex chains from basic components, and supports out of the box functionality such as streaming, parallelism, and logging.
LCEL is a domain-specific language that provides several key advantages when working with LangChain:
- Composability: It allows you to easily combine different LangChain components like retrievers, language models, and output parsers into complex workflows.
- Readability: The syntax is concise and expressive, making it easy to understand the flow of operations within a chain or sequence.
- Reusability: You can define reusable sub-chains or components that can be incorporated into larger chains, promoting code reuse and modularity.
In summary, LCEL streamlines the process of building sophisticated natural language processing applications by providing a composable, readable, reusable, extensible, type-safe, and abstracted way to define and orchestrate LangChain components into complex workflows.
We will be using LCEL chains in next few sections and will see how LCEL optimizes our whole workflow.
Create Retriever Chain
We also create the retriever of the couchbase vector store. This retriever will be used to retrieve the previously added documents which are similar to current query.
retriever = vector_store.as_retriever()Prompt Chain
A prompt for a language model is a set of instructions or input provided by a user to guide the model's response, helping it understand the context and generate relevant and coherent language-based output, such as answering questions, completing sentences, or engaging in a conversation. We will use a template and create a prompt chain using ChatPromptTemplate Class of LangChain
template = """You are a helpful bot. If you cannot answer based on the context provided, respond with a generic answer. Answer the question as truthfully as possible using the context below:
{context}
Question: {question}"""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)LLM Chain
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a core component of LangChain. LangChain does not serve its own LLMs, but rather provides a standard interface for interacting with many LLMs. To be specific, this interface is one that takes as input a string and returns a string. We will use Meta's LLama3 LLM Model powered and inferenced using Nvidia's NIM Infrastructure. We can also set other parameters like model, API_KEY, temperature to be used for this model.
llm = ChatNVIDIA(temperature=0, model="meta/llama3-70b-instruct"Combining to a single chain
We can combine these different modules to a single chain which will run synchronously. The pipe operator (|) is used to connect these components, forming a chain of operations.
The input dictionary with the "context" and "question" keys is passed through each component. The retriever component retrieves relevant information from the vector store, which is then combined with the question to generate a prompt. This prompt is passed to the language model (llm), which generates a response based on both the question and the retrieved context. Finally, the output is parsed into a string by StrOutputParser().
# RAG chain
chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)User Asks A Question
This section creates an interactive chat interface where users can ask questions based on the uploaded PDF. The key steps are:
- Display a chat input box with the prompt "Ask a question based on the PDF".
- When the user submits a question:
- Display the user's question in the chat interface
- Add the user's question to the chat history.
- Create a placeholder for streaming the assistant's response.
- Use the chain.stream(question) method to generate the response from the RAG chain.
- Stream the response in real-time by updating the placeholder with each response chunk.
- Add the final assistant's response to the chat history.
This setup allows users to have a conversational experience, asking questions related to the uploaded PDF, with responses generated by the RAG chain and streamed in real-time. Both the user's questions and the assistant's responses are displayed in the chat interface, along with their respective roles and avatars.
# React to user input
if question := st.chat_input("Ask a question based on the PDF"):
# Display user message in chat message container
st.chat_message("user").markdown(question)
# Add user message to chat history
st.session_state.messages.append(
{"role": "user", "content": question, "avatar": "👤"}
)
# Add placeholder for streaming the response
with st.chat_message("assistant", avatar=couchbase_logo):
message_placeholder = st.empty()
# stream the response from the RAG
rag_response = ""
for chunk in chain.stream(question):
rag_response += chunk
message_placeholder.markdown(rag_response + "▌")
message_placeholder.markdown(rag_response)
st.session_state.messages.append(
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": rag_response,
"avatar": couchbase_logo,
}
)