Couchbase Lite Query Builder Engine with Dart and Flutter
- Learn how to query documents in Couchbase Lite
- Explore the Query Builder Engine
Introduction
Couchbase Lite brings powerful querying and Full-Text-Search(FTS) capabilties to the edge. The query builder interface is based on SQL++, Couchbase’s declarative query language that extends SQL for JSON. If you are familiar with SQL, you will feel right at home with the semantics of the new API. The query builder API is designed using the Fluent API Design Pattern, and it uses method cascading to read to like a Domain Specific Language (DSL). This makes the interface very intuitive and easy to understand.
In this step of the learning path you will learn the fundamentals of:
- Using the QueryBuilder API
- Using Live Queries with streams
- Using JSON Serialization to "deserialize" documents from the database in to dart classes
- Using indexes to speed up a query
- Using the count function with the QueryBuilder API
- Using the LIKE operator to search for documents with a specific value in a field
App Overview
While the demo app has a lot of functionality, this step will walk you through:
- Log in into the application
- Scrolling the list of projects
- Review the code for displaying projects
NOTE: This step assumes you completed the previous step
Batch operationsthat loaded the sample data into the application. This part of the learning path will not work if you don't complete the previous steps.
Installation
Fetching App Source Code
Clone Source Code
- If you haven't already cloned the repo from the previous step, clone the
Learn Couchbase Lite with Dart and Flutterrepository from GitHub.
git clone https://github.com/couchbase-examples/flutter_cbl_learning_path.gitTry it out
- Open src folder using your favorite IDE
- Build and run the project.
- Log in to the app with "demo@example.com" and "P@ssw0rd12" for user Id and password fields respectively.
- Verify that you see sample projects on the screen. If you do not see sample projects, please complete the previous step Batch operations to load sample data before continuing.
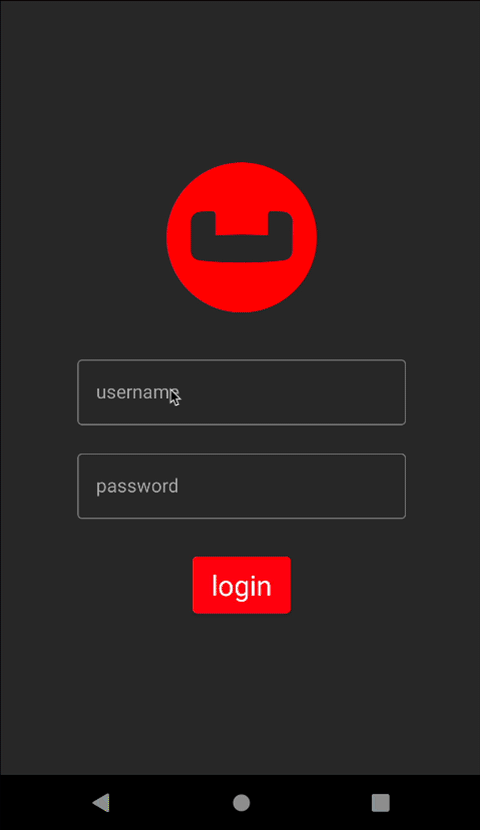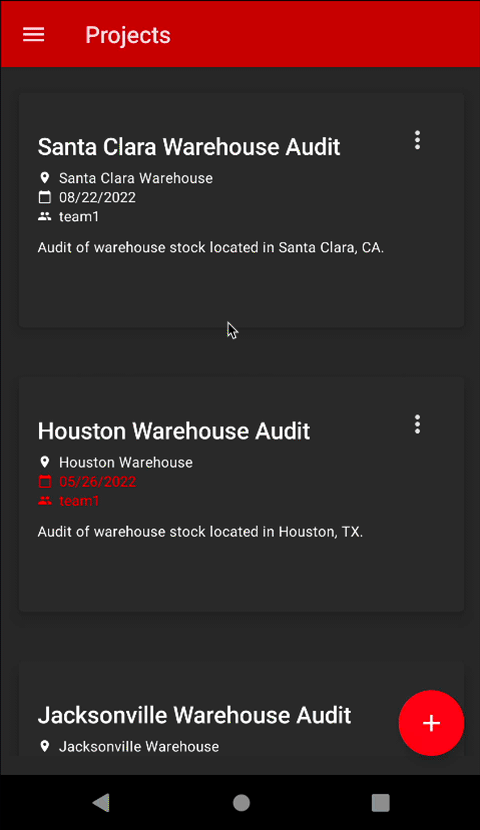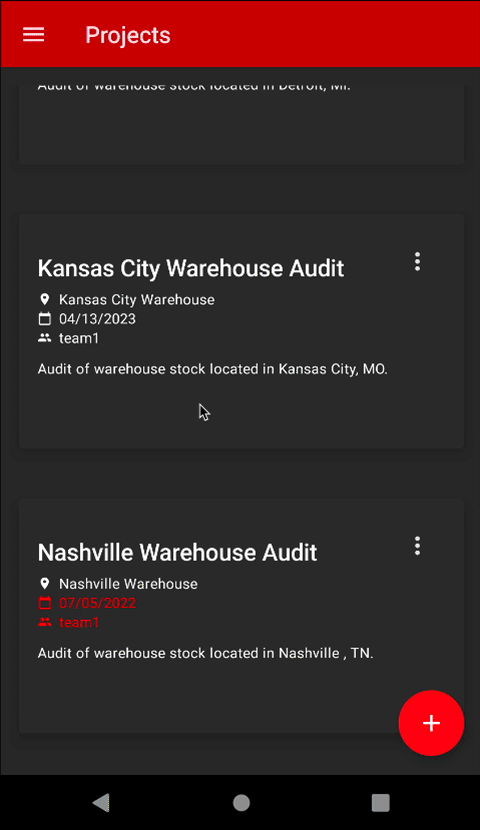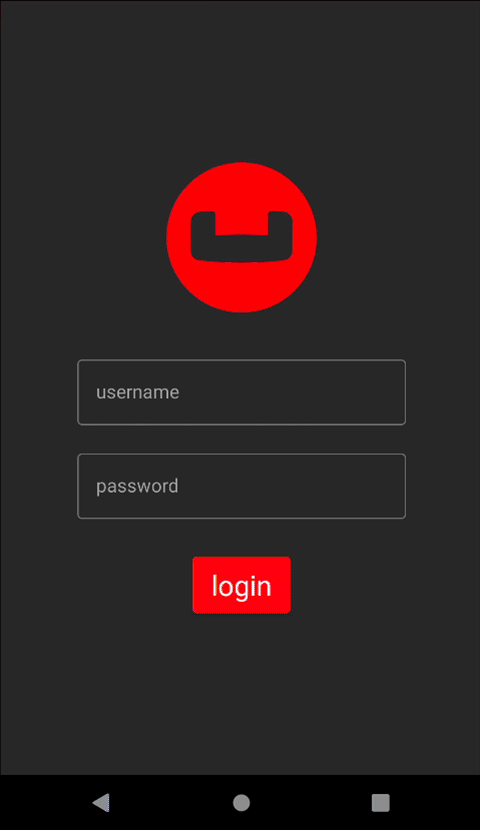
Data Model
A reminder that Couchbase Lite is a JSON Document Store. A Document is a logical collection of named fields and values. The values are any valid JSON types. In addition to the standard JSON types, Couchbase Lite supports Date and Blob data types. While it is not required or enforced, it is a recommended practice to include a "documentType" property that can serve as a namespace for related documents.
The Project Document
The sample app was loaded with a collection of Document with a "documentType" property of "project" in the previous step. Each document represents a project that a team would would work on and have to complete before the due date based on a selected location, which is another document type.
An example of a document would be:
{
"team": "team1",
"modifiedOn": "2022-10-12",
"documentType": "project",
"createdBy": "demo@example.com",
"dueDate": "2022-10-31",
"name": "Santa Clara Warehouse Audit",
"description": "Audit of warehouse stock located in Santa Clara, CA.",
"modifiedBy": "demo@example.com",
"warehouse": {
"documentType": "warehouse",
"name": "Santa Clara Warehouse",
"shippingTo": [
"AZ",
"CA",
"HI",
"NV"
],
"warehouseId": "e1839e0b-57a0-472c-b29d-8d57e256ef32",
"city": "Santa Clara",
"address1": "3250 Dr Olcott Street",
"postalCode": "95054",
"latitude": 32.3803024,
"state": "CA",
"salesTax": 0.0913,
"longitude": -121.9674197,
"yearToDateBalance": 0.0
},
"projectId": "663953ba-9e4c-4090-9e07-642c1778d467",
"createdOn": "2022-10-10"
}The Project Data Class
When a "project" is retreived from the database it is stored within an data class of type Project.
(explicitToJson: true)
class Project {
String projectId;
String name;
String description;
bool isComplete;
String documentType = 'project';
DateTime? dueDate;
Warehouse? warehouse;
//security tracking
String team;
String createdBy;
String modifiedBy;
DateTime? createdOn;
DateTime? modifiedOn;
Project( {
required this.projectId,
required this.name,
required this.description,
required this.isComplete,
required this.dueDate,
required this.warehouse,
required this.team,
required this.createdBy,
required this.createdOn,
required this.modifiedBy,
required this.modifiedOn});
String dueDateToString() {
var date = dueDate;
if (date != null) {
return '${date.month}/${date.day}/${date.year}';
}
return '';
}
factory Project.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) =>
_$ProjectFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$ProjectToJson(this);
}The Warehouse Class
When a "warehouse" from a project is retreived from the database it is stored within a data class of type Warehouse.
(explicitToJson: true)
class Warehouse {
final String warehouseId;
final String name;
final String address1;
final String? address2;
final String city;
final String state;
final String postalCode;
final double salesTax;
final double yearToDateBalance;
final double latitude;
final double longitude;
final List<String>? shippingTo;
final String documentType = "warehouse";
const Warehouse(
this.warehouseId,
this.name,
this.address1,
this.address2,
this.city,
this.state,
this.postalCode,
this.salesTax,
this.yearToDateBalance,
this.latitude,
this.longitude,
this.shippingTo);
String toString(){
return name;
}
factory Warehouse.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) =>
_$WarehouseFromJson(json);
Map<String, dynamic> toJson() => _$WarehouseToJson(this);
}Exploring the Query Builder API with the Count Function
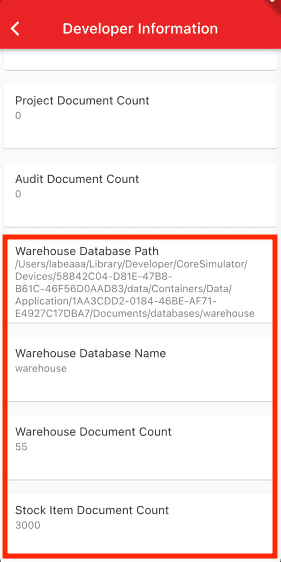
The Query API in Couchbase Lite is extensive. On the Developer - Database Information screen we display the number of warehouse documents found in the warehouse database. The QueryBuilder API along with the count function was used to calculate this number. To see the Developer Information screen:
- Launch the Invenory Application on your Android emulator or iOS simulator.
- Login in using the username demo@example.com and password P@ssw0rd12
- Click the Drawer menu icon (sometimes referred to the Hamburger icon) and tap on Developer
- Tap on the Database Information button
Counting number of documents by type
The "DeveloperInfoWidget" screen displays the count of how many documents are in the warehouse database with the type set to 'warehouse'.
The DeveloperInfoWidget class obtains this information from the DevInfoBloc class, which emits this information. The DevInfoBloc calls the WarehouseRepository which runs the query to calculate the count.
final warehouseCounter = await _warehouseRepository.count();- Open the warehouse_repository.dart file and locate the
countfunction.
Future<int> count() async {- We build the Query using the
QueryBuilderAPI that will look for Documents that match the specified criteria.
var count = 0;
try {
const attributeCount = 'count';
final db = _databaseProvider.warehouseDatabase;
if (db != null) {
final query = QueryBuilder.createAsync()
.select(
SelectResult.expression(Function_.count(Expression.string("*")))
.as(attributeCount))
.from(DataSource.database(db))
.where(Expression.property(attributeDocumentType)
.equalTo(Expression.string(documentType))); // <1>
final result = await query.execute(); // <2>
final results = await result.allResults(); // <3>
count = results.first.integer(attributeCount); // <4>
}
} catch (e) {
debugPrint(e.toString());
}
return count;- Call the Query Builder API to create a Query
- Call the
executefunction to execute the query - Call the
allResultsfunction to get all the results from the query - We get the results by looking at the first result in the collection and getting an integer value for the key which we defined in the
selectclause asattributeCount.
Further Exploring the Query Builder API - return List of Projects Documents
The Query Builder API in Couchbase Lite is extensive. In our second example, we will be using the QueryBuilder API to make a simple pattern matching query using the equalTo operator. This example will use Live Query with dart streams.
Fetching Project Documents
From the "Login" screen, when a user logs in with the proper credentials they are presented with a list of projects there team is assigned to work on.
-
Open the project_list_widget.dart file and locate the
buildfunction. -
The live query is an AsyncListenStream
which is emit to state as List in the ProjectListBloc.
TIP: Anytime documents change or are added to the database that satisify this query, the listen(change) would fire in the ProjectListBloc and the ProjectListBloc would fire the ProjectListLoadedEvent that would update state. The
live queryAPI can dynmamically update your UI without the need for end user interaction, which will come in handy in future sections of the learning path when we review replication.
case DataStatus.loaded:
case DataStatus.changed:
return SafeArea(
child: ListView.builder(
itemCount: state.items.length,
itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () => {
routerService.routeTo(ScreenRoute(
routeToScreen: RouteToScreen.audits,
projectId: state.items[index].projectId,
auditListBloc:
BlocProvider.of<AuditListBloc>(context)))
},
child: ProjectCard(
project: state.items[index],
routerService: routerService));
}));- To see how the
List<Project>items is created, open the project_list_bloc.dart file and locate the_onInitializemethod.
Future<void> _onInitialize(
ProjectListInitializeEvent event,
Emitter<ProjectListState> emit) async {- The bloc listens to the stream provided by the
ProjectRepository.getDocuments()method.
if (_liveQueryStream == null) {
// <1>
_liveQueryStream = await _repository.getDocuments();
// <2>
if (_liveQueryStream != null) {
// <3>
var stream = _liveQueryStream;
emit(state.copyWith(status: DataStatus.loading));
// <4>
stream?.listen((change) async {
// <5>
var items = <Project>[];
// <6>
var results = await change.results.allResults();
// <7>
for (var result in results) {
// <8>
var map = result.toPlainMap();
var dao = ProjectDao.fromJson(map);
// <9>
items.add(dao.item);
}
// <10>
if (!isClosed) {
add(ProjectListLoadedEvent(items: items));
}
});
//await stream?.listening;
}
}- Check the _liveQueryStream to see if it is null. If it is null, then we will create a new stream, otherwise we assume the stream is already setup and being listened to.
- Set the _liveQueryStream to the
AsyncListenStreamofQueryChange<ResultSet>returned by theProjectRepository.getDocuments()method. - Get a local reference to the stream for nully checking purposes.
- Listen to the stream for changes via the
changeparameter. - Create local variable to hold the list of Project items.
- Get the
ResultSetfrom the change object. - Loop through the results in the Result Set.
- Convert the results to a plain map and then to a DOA (Data Access Object).
- Add the Project item to the list.
- If the bloc is not closed, then emit the ProjectListLoadedEvent with the list of Project items. The bloc could be closed for several reasons including the app going to the background. If the change fires reason while the app is in the background, this would be bad since the application is not in the foreground and the UI can't be updated. The
isClosedcheck prevents this from happening.
- To see how to build a live query that returns a stream, open the project_repository.dart file and locate the getDocuments function.
Future<AsyncListenStream<QueryChange<ResultSet>>?>? getDocuments() async {- We first build a Query using the
QueryBuilderAPI that will look for Documents that match the specified criteria.
var query = QueryBuilder.createAsync() //<1>
.select(SelectResult.all()) //<2>
.from(DataSource.database(db).as('item')) //<3>
.where(Expression.property(attributeDocumentType)
.equalTo(Expression.string(projectDocumentType))
.and(Expression.property('team')
.equalTo(Expression.string(team)))); // <4>
return query.changes(); // <5>- Create a query using the
QueryBuilderAPI and the createAsync method. - The
SelectResult.all()specifies that we are interested in all properties in Documents that match the specified criteria - The DataSource.database(db).as('item') specified the Data Source.
- The
Expressionbuilds aQueryExpressionused to find documents where thedocumentTypeproperty and theteamproperties are equal to the values passed in - Return any changes to the documents that match this criteria by callling the
query.changes()method which returns the AsyncListenStream of QueryChange.
Indexing the Query
-
Creating indexes for non-FTS based queries is optional. However, to speed up queries, you can create indexes on the properties that you would query against. Indexing is handled eagerly.
-
In the database_provider.dart file, locate the
_createTeamDocumentTypeIndexmethod. -
We create an index on the
documentTypeandteamproperties of the documents in the inventory database.
Future<void> _createTeamDocumentTypeIndex() async {
final documentTypeExpression =
Expression.property(documentTypeAttributeName); //<1>
final teamExpression = Expression.property( teamAttributeName); //<2>
final valueIndexItems = {
ValueIndexItem.expression(documentTypeExpression),
ValueIndexItem.expression(teamExpression)
}; //<3>
final index = IndexBuilder.valueIndex(valueIndexItems); //<4>
var inventoryDb = inventoryDatabase; //<5>
if (inventoryDb != null) { //<6>
final indexes = await inventoryDb.indexes; //<7>
if (!(indexes.contains(teamIndexName))) { //<8>
await inventoryDb.createIndex(teamIndexName, index); //<9>
}
}
}- Create the expresion for the
documentTypeattribute. - Create the expression for the
teamattribute. - Create a collection of valueIndexItems to set the index to.
- Create the index using the IndexBuilder API.
- Get a reference to the inventory database for null checking purproses.
- Check the database to make sure it's not null
- Get the list of indexes from the database. We don't want to try to create the index if it already exists.
- Check to see if the index already exists.
- If the index doesn't exist, then create it.
Query Builder API - Searching for Warehouses with the LIKE Operator
The Query Builder API supports serveral operators including the LIKE which can be used for string matching. We use the LIKE operator on the data editor screen for Projects to find a warehouse to add to a project. Let's review the code.
NOTE: The like operator performs case sensitive matches. To perform case insensitive matching, use lowercase or uppercase functions to ensure all comparators have the same case, thereby removing the case issue.
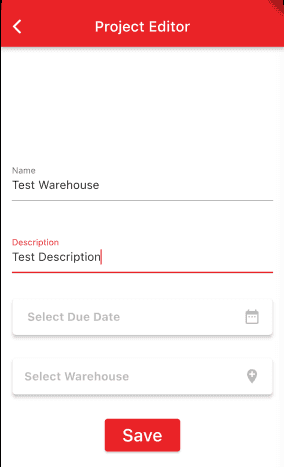
On the Project Editor screen we provide a link to the Warehouse Section screen. To see the Project Editor screen:
- Launch the Invenory Application on your Android Emulator or iOS Simulator.
- Login in using the username demo@example.com and password P@ssw0rd12
- Click the + icon to add a Project
- Type in a name for the project on the Name field.
- Tap the button
Select Warehouse
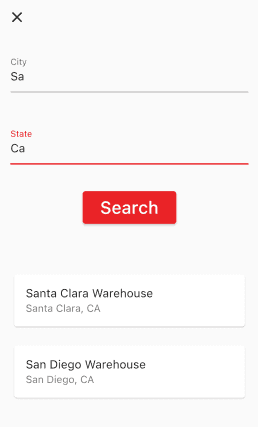
- In the City box enter Sa
- In the State box enter Ca
- Hit the Search button
- A listing of warehouses should return that match these results
Let's review the code for the Warehouse Section screen.
Warehouse Selection
-
Open the project_editor_form.dart file and locate the
_WarehouseSearchButtonclass. -
The build method adds an Elevated Button
-
The onPressed method adds the blocs WarehouseSearchSubmitChangeEvent when a user taps on the Search button.
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BlocBuilder<WarehouseSearchBloc, WarehouseSearchState>(
builder: (context, state) {
if (state.status == FormEditorStatus.dataSaved ||
state.status == FormEditorStatus.cancelled) {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
return const Text('');
} else {
return Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(top: 16.0, left: 8.0, right: 8.0),
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
context
.read<WarehouseSearchBloc>()
.add(const WarehouseSearchSubmitChangedEvent());
},
child: const Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Text(
"Search",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white, fontSize: 24.0),
))),
);
}
});
}- Open the warehouse_search_bloc.dart file and locate the
_onSubmittedmethod.
FutureOr<void> _onSubmitted(
WarehouseSearchSubmitChangedEvent event,
Emitter<WarehouseSearchState> emit) async {
if (state.searchCity.isNotEmpty) { // <1>
//get warehouse list from repository
try {
var items =
await _repository.search(state.searchCity, state.searchState); // <2>
if (items.isNotEmpty) {
emit(state.copyWith(
error: '',
status: FormEditorStatus.dataLoaded,
warehouses: items)); //<3>
} else {
emit(state.copyWith(
error: 'No warehouses found matching criteria.',
status: FormEditorStatus.error)); //<4>
}
} catch (e) {
emit(state.copyWith(
error: e.toString(), status: FormEditorStatus.error));
}
} else {
emit(state.copyWith(
error: 'Error - City can\'t be blank',
status: FormEditorStatus.error));
}
}- Check to make sure that the city field is not empty. If it is, then we can't search for a warehouse as city is a required field.
- Call the repository to search for warehouses. The repository will use the Query Builder API to search for warehouses.
- If the search returns a list of warehouses, then emit the state with the list of warehouses.
- If not, then emit the state with an error message.
- Open the warehouse_repository.dart file and locate the
searchmethod.
Future<List<Warehouse>> search(String searchCity, String? searchState) async {- This method does not use live query, so we return a List of Warehouse objects.
List<Warehouse> items = [];
try {
var db = _databaseProvider.warehouseDatabase;
if (db != null) {
// <1>
var whereExpression = Function_
.lower(Expression.property(attributeDocumentType))
.equalTo(Expression.string(documentType));
// <2>
var cityExpression = Function_
.lower(Expression.property(cityAttributeName))
.like(Expression.string("%${searchCity.toLowerCase()}%"));
whereExpression = whereExpression.and(cityExpression);
// <3>
if(searchState != null && searchState.isNotEmpty){
var stateExpression = Function_.lower(Expression.property(stateAttributeName))
.like(Expression.string("%${searchState.toLowerCase()}%"));
whereExpression = whereExpression.and(stateExpression);
}
// <4>
var query = QueryBuilder.createAsync()
.select(SelectResult.all())
.from(DataSource.database(db).as('warehouse'))
.where(whereExpression);
// <5>
var result = await query.execute();
var results = await result.allResults();
// <6>
for (var r in results) {
var map = r.toPlainMap();
var warehouseDoa = WarehouseDao.fromJson(map);
items.add(warehouseDoa.warehouse);
}
}
} catch (e) {
debugPrint(e.toString());
}
return items;- Create a query expression off the type attribute and use the equalTo function to pass in the documentType value. This makes sure we only match warehouse documents.
- Create a query expression off the city attribute and use the like function to pass in the searchCity value. We make sure to use the searchCity toLowerCase method to make the search case insensitive.
- If the searchState value is not null, then we will create a query expression off the state attribute and use the like function to pass in the searchState value. We make sure to use the searchState toLowerCase method to make the search case insensitive.
- We will build a query using the QueryBuilder API to select all the results from the database and pass in our whereQueryExpression with our like statement(s).
- We loop through all the results and add them to the warehouses list that is then returned.
Learn More
Congratulations on completing this step of our learning path!
This step of the learning path walked you through the Query Builder API in Couchbase Lite and used it to return documents from the database and we looked at calling the Query API built-in count function. Check out the following links for further documenation and continue on to the next step to learn more about how to use Query Builder with SQL++ syntax.